SYSTEMD: Mother of all processes
systemd is the replacement system for System V and with the primary goal of starting services in parallel.
Remember
initlevels?
GRUB: Grand Unified Boot Loader
/boot/grub/grub.conf
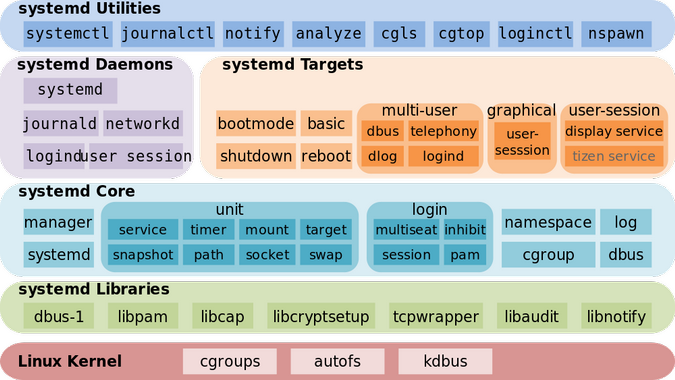
Some key points
systemdis PID 1- Major points in a boot-up process
- There are two sequences of events that are required to boot a Linux computer and make it usable: boot and startup.
- The boot sequence starts when the computer is turned on, and is completed when the
kernelis initialized and systemd is launched. - startup process takes over after
bootis complete and finishes the task of getting the Linux computer into an operational state. - BIOS – Power on self test
- BIOS POST checks the basic operability of the hardware and then it issues an interrupt, which locates the boot sectors on any attached bootable devices
- Boot loader
- First stage – The first boot sector with valid boot record (MBR) is loaded into RAM and control is then transferred to the code that was loaded from the boot sector.
- Kernel Initialization
- The primary function of boot loader like GRUB is to get the Linux kernel loaded into memory and running.
- Once the kernel has extracted itself, it loads systemd, and turns control over to it.
- Start
systemd– mother of all processes.- It is responsible for bringing the Linux host up to a state in which productive work can be done.
- First
systemdmounts the filesystems as defined by /etc/fstab
ls /etc/systemd
total 40
0 drwxr-xr-x. 4 root root 151 Aug 31 08:45 .
12 drwxr-xr-x. 145 root root 8192 Aug 31 08:46 ..
4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 720 Aug 6 17:30 bootchart.conf
4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 615 Aug 6 17:30 coredump.conf
4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 983 Aug 6 17:30 journald.conf
4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 968 Jan 28 2019 logind.conf
4 drwxr-xr-x. 19 root root 4096 Aug 6 17:30 system
4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1552 Aug 6 17:30 system.conf
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Aug 6 17:30 user
4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1127 Aug 6 17:30 user.confIf POST fails, the computer may not be usable and so the boot process does not continue.
Example: /etc/fstab
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Mon Jan 28 20:51:49 2019
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
UUID=f41e390f-835b-4223-a9bb-9b45984ddf8d / xfs defaults 0 0Note that targets and services are
systemdunits.
Targets: /etc/systemd/system
root@docker>ls -als system
total 16
4 drwxr-xr-x. 19 root root 4096 Aug 6 17:30 .
0 drwxr-xr-x. 4 root root 151 Aug 31 08:45 ..
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 57 Jan 28 2019 basic.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 31 Mar 18 2019 bluetooth.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 119 Jul 28 07:54 cloud-init.target.wants
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 41 Mar 18 2019 dbus-org.bluez.service -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/bluetooth.service
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 41 Mar 18 2019 dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 44 Mar 18 2019 dbus-org.freedesktop.Avahi.service -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/avahi-daemon.service
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 44 Mar 18 2019 dbus-org.freedesktop.ModemManager1.service -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/ModemManager.service
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 46 Mar 18 2019 dbus-org.freedesktop.NetworkManager.service -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/NetworkManager.service
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 57 Mar 18 2019 dbus-org.freedesktop.nm-dispatcher.service -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 37 Jan 28 2019 default.target -> /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 111 Mar 18 2019 default.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 38 Jan 28 2019 dev-virtio\x2dports-org.qemu.guest_agent.0.device.wants
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 35 Mar 18 2019 display-manager.service -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/gdm.service
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 32 Jan 28 2019 getty.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 133 Mar 18 2019 graphical.target.wants
4 -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 435 Mar 18 2019 ir_agent.service
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 35 Jan 28 2019 local-fs.target.wants
4 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Jul 30 11:02 multi-user.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 48 Mar 18 2019 network-online.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 26 Mar 18 2019 printer.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 31 Jan 28 2019 remote-fs.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 217 Mar 18 2019 sockets.target.wants
4 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Mar 18 2019 sysinit.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 44 Jan 28 2019 system-update.target.wants
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 34 Mar 18 2019 timers.target.wants
0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 9 Jan 28 2019 tmp.mount -> /dev/null
0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 29 Mar 18 2019 vmtoolsd.service.requires/etc/systemd/system/default.target
# This file is part of systemd.
#
# systemd is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
# under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
[Unit]
Description=Multi-User System
Documentation=man:systemd.special(7)
Requires=basic.target
Conflicts=rescue.service rescue.target
After=basic.target rescue.service rescue.target
AllowIsolate=yesThe After & Requires defines the dependencies.
One thought on “SYSTEMD: Mother of all processes”
Comments are closed.

Files in /etc have highest priority, files in /run have the second highest priority, …, files in /lib have lowest priority.